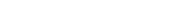-
About Us
About Us
The word “Amicogen” consists of the meaning of friend, “AMICO”
in Latin and of gene, “GENE”. We developed innovative biocatalysts
and proteins by applying our proprietary i DNA Evolution™ Technology.
We are a “Bioengineering company just like a Sincere Friend”
who contributes to the human health and the preservation of environment. Amicogen is the representative Industrial Biotechnology Company in Korea
Amicogen is the representative Industrial Biotechnology Company in Korea
and wants to contribute to the protection of human health and the environment. -
R&D
R&D
Amicogen Biotech R&D Center is expanding its R&D field based on
bio-platform technology, and researchers account for 30% of all employees.
We will lead the Industrial Biotechnology to develop new technologies
that can drive the development of humanity and society,
one step further than others. Amicogen continues innovative research
Amicogen continues innovative research
and development for its first and best products. -
Products
Products
Amicogen has developed Special Enzymes for industrial and pharmaceutical products based on the i DNA evolution™.
We want to contribute to the sustainable growth and lifelong health
of humanity by developing New Bio-Ingredientfor Health functional foods
with Special Enzymes and Protein Purification Resin. Amicogen develops Bio Products and
Amicogen develops Bio Products and
New Bio-Ingredients for Health functional food. -
Investors
Investors
As Amicogen started as a bio-venture company, we have focused on
the core competence of R&D and are pursuing sustainable growth
in innovative technologies and products. To increase the value
of enterprise and shareholder, we are continually strengthening our core competencies such as specialty enzyme business, healthcare, protein
purification resin business and others. Amicogen strengthens key capacities
Amicogen strengthens key capacities
to increase enterprise value and shareholder value. -
Media
Media
Amicogen promotes various activities to realize the value of contributing
to the protection of human health and the environment.
Amicogen is positioning itself as a global biotechnology company
through growth and leaps to create new values. You can find various looks and news of Amicogen
You can find various looks and news of Amicogen
taking the initiative in the global bio industry. -
ESG
Sustainable management
Amicogen has developed bio innovative technologies and operated the businesses that consider humankind and environment from the perspective of sustainability for the past 20 years. We will continue sustainable development based on Amicogen's environmental soundness, social responsibility and sustainable innovative technology.
 Amicogen wants to contribute to the protection of human health and the environment.
Amicogen wants to contribute to the protection of human health and the environment. -
Careers
Careers
Amicogen produces new technologies and values based on
creative thinking and constant technological innovation through human
oriented management. We do our best to ensure that talented individuals
with unique skills and abilities can demonstrate their abilities
according to the nature of their duties. We are waiting for Amicogen people,
We are waiting for Amicogen people,
who will open new values and a bright future. -
CONTACT
Careers
Amicogen produces new technologies and values based on
creative thinking and constant technological innovation through human
oriented management. We do our best to ensure that talented individuals
with unique skills and abilities can demonstrate their abilities
according to the nature of their duties. We are waiting for Amicogen people,
We are waiting for Amicogen people,
who will open new values and a bright future.
Bio Research & Innovation
Bio Research & Innovation
Amicogen's power of growth begins with R&D.
We will continue the innovative R&D for the first and best products.
Gene evolution technology
These genes are repeatedly, genetically engineered in a variety of forms through the recombination process called sexual reproduction.
Under these mutants, if it meets the selection criteria of the natural environment, it will be dominating species, otherwise it will disappear.
In other words, organisms generate genetic diversity through genetic mutation and gene evolution processes, genetic diversity is selected
through selection criteria of the natural environment, and more developed excellent genes are created.
These methods of natural evolution will take millions of years for a given gene to improve in a particular direction.
“Gene evolution” refers to a technique for artificially accelerating the naturally occurring recombination phenomena in a laboratory of laboratories
to select genes with the properties we desire in a short time.”
- By obtaining a group of genes with different mutations and
- Making different recombinant DNA libraries by exchanging different mutations of these gene groups
- It is a technology to select useful genes with the necessary properties from this library.
Enzyme reaction technology
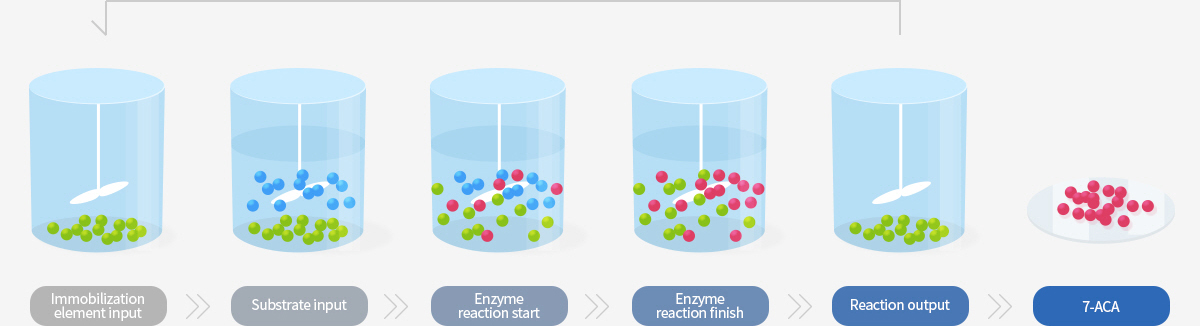
First, the reactor must be developed that can continuously improve temperature, pH, substrate entry, and the recovery of reaction products.
It is possible to improve the yield and quality of the reaction products by efficient enzyme reaction through the optimization of all processes
as to whether the substrate to be used is water-soluble or insoluble, the amount of enzyme to be added, the concentration of the substrate to be added,
the input rate and the speed of stirring.
Mass production technology of enzyme and protein

In order to achieve this, it is possible to culture the microorganisms in which the enzyme is first expressed, i.e., fermentation by mass production.
It can make mass production at a low cost by maximizing the culture conditions of various microorganisms
such as appropriate culture medium, various nutrients for cultivation, bath pH, culture temperature and oxygen demand.
Enzymes produced by the way of mass fermentation must be separated and purified by various methods, depending on
whether they are expressed intracellularly or secreted on other cells.
When secreted in addition to cells, it is only necessary that cells are removed and only the culture solution is recovered and purified,
but when expressed in the cells, it needs complicated process such as recovery of cells, destruction of cells, destruction of minced cell debris
and removal of various nucleic acid substances to separate and purify with a clean and high purity enzyme.
Development of immobilized enzyme and mass production technology

which in turn increases competitiveness compared to technology with chemical processes.
In order to reuse water-soluble enzymes and proteins, it is necessary to immobilize them on insoluble carriers to separate them from the reaction products.
In the case of immobilizing the enzyme, it can be easily separated from the reaction product and can be continuously reused.
In particular, it can increase the cycle by apparent increase of the stability due to external conditions such as temperature, pH, pressure, etc.
However, there are disadvantages that the active site of the enzyme is inactivated by deformation or the reaction efficiency reduced due to a decrease in substance diffusion.
The nature of the carrier used for the immobilization and the immobilization method varies depending on the type of enzyme, used protein and the reaction system.
In addition to it, the properties such as carrier size, pore size, affinity, strength and etc depending on the reaction system of the enzyme should be optimized so that the immobilized enzyme can be used efficiently.